Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it? This respiratory virus, similar to RSV and influenza, is causing concern. Let’s explore what HMPV is, how it spreads, its symptoms, and what’s happening in China. Understanding this virus is key to protecting children, especially in crowded environments like schools and daycare centers.
We’ll cover the virus’s characteristics, transmission methods, and the symptoms it causes in children of different ages. We’ll also discuss diagnosis, treatment options, and importantly, preventative measures parents can take to safeguard their little ones. Finally, we’ll delve into the specifics of the current situation in China and the public health response.
So, HMPV is causing a surge in childhood illnesses in China – it’s a respiratory virus, similar to RSV. While doctors are busy dealing with that, check out this amazing celestial event – Venus Moon duo and Quadrantids meteors stun stargazers – a welcome distraction from the news, though hopefully, the HMPV outbreak will ease soon.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV): A Rising Threat to Children in China
The recent surge in Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) cases among children in China highlights the importance of understanding this respiratory virus. This article provides a comprehensive overview of HMPV, including its characteristics, transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention, with a specific focus on the current situation in China.
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV): An Overview
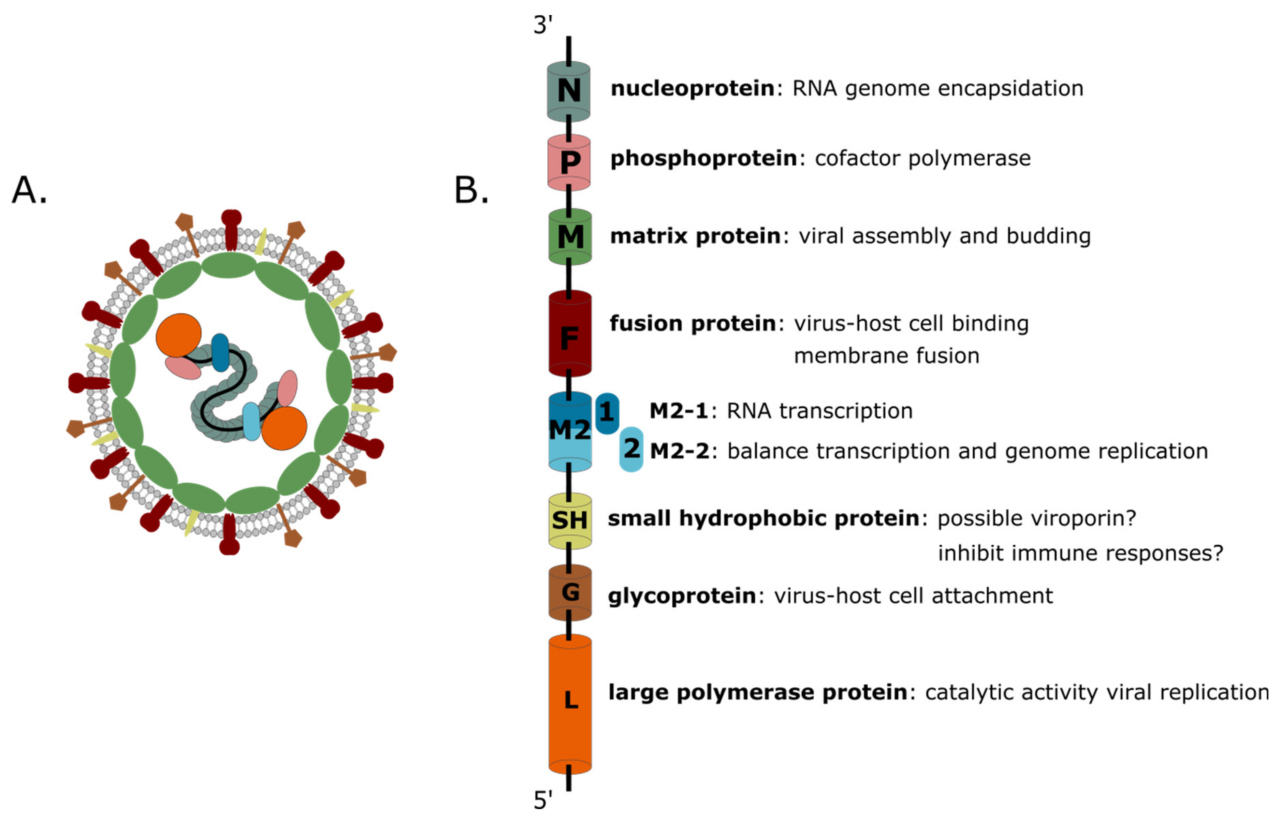
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common respiratory virus belonging to the Paramyxoviridae family. It’s a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus, meaning its genetic material is RNA and the RNA strand is complementary to the mRNA used in protein synthesis. The virus particle is enveloped, meaning it has a lipid bilayer membrane surrounding its core. This envelope contains proteins essential for attachment to and entry into host cells.
HMPV exists in two major genotypes, A and B, each with further subtypes. Genotype A is further divided into A1 and A2, while genotype B is subdivided into B1 and B2. These genetic variations can influence the severity of infection and the immune response.
Compared to other respiratory viruses like RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus) and influenza, HMPV shares similar transmission routes and clinical manifestations, often causing similar symptoms such as cough, fever, and shortness of breath. However, specific symptoms and severity can vary. HMPV is generally considered less severe than RSV in infants, but it can still lead to significant respiratory illness.
| Virus Type | Transmission Method | Symptoms | Severity | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) | Respiratory droplets, contact | Cough, fever, runny nose, shortness of breath | Mild to severe, potentially life-threatening in infants | Supportive care, antiviral medications in severe cases |
Transmission and Spread of HMPV
HMPV primarily spreads through respiratory droplets produced during coughing or sneezing. Close contact with infected individuals facilitates transmission. Crowded environments, such as schools and daycare centers, significantly increase the risk of spread due to the high density of susceptible individuals and frequent close contact. Infants, young children, the elderly, and individuals with underlying respiratory conditions are particularly vulnerable.
So, HMPV is causing a surge in childhood illnesses in China – it’s a respiratory virus, kinda like RSV. Want a break from worrying about viruses? Check out this game analysis: Milan 2-1 Juventus (Jan 3, 2025) Game Analysis – ESPN. Back to HMPV, though – understanding its spread is key to managing this outbreak.
Infographic depicting the transmission cycle of HMPV: The infographic would use a circular flow chart. The center would depict a person infected with HMPV, represented by a red circle with a virus icon. Arrows would radiate outwards to depict various transmission routes: direct contact (represented by a hand reaching out to touch the infected person), respiratory droplets (represented by small blue spheres emanating from the infected person’s mouth), and contaminated surfaces (represented by a yellow surface with a virus icon).
Each transmission route would be labeled clearly. The color scheme would be predominantly blue and red, to represent the respiratory system and the virus, respectively. The font would be clear and easy to read.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations of HMPV, Viral disease HMPV is on the rise among kids in China — what is it?
Common symptoms in children include cough, fever, runny nose, and shortness of breath. Infants may exhibit more severe symptoms, including difficulty breathing, wheezing, and dehydration. Older children might experience milder symptoms, similar to a common cold. Potential complications include bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and respiratory distress.
Okay, so you’re wondering about HMPV, that viral disease hitting kids in China? It’s a respiratory virus, kind of like RSV. While that’s concerning, it’s a good reminder that global health is complex; for example, check out this interview with Pierre Poilievre where he discusses his political goals: Pierre Poilievre dévoile ses objectifs dans une entrevue accordée à.
Anyway, back to HMPV – keeping up with these outbreaks requires staying informed about various global issues.
- Mild HMPV Infection: Runny nose, mild cough, low-grade fever.
- Moderate HMPV Infection: Persistent cough, higher fever, increased respiratory rate.
- Severe HMPV Infection: Difficulty breathing, wheezing, rapid breathing, cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin).
Diagnosis and Treatment of HMPV
Diagnosis is typically made through laboratory testing, such as PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) or antigen detection tests, on respiratory samples. Treatment primarily involves supportive care, including hydration, rest, and fever reduction. Antiviral medications may be considered in severe cases to reduce the duration and severity of the illness. Supportive care focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Prevention and Control Measures for HMPV
Key preventive measures include frequent handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. While there is currently no HMPV vaccine, promoting good hygiene practices is crucial in controlling the spread of the virus. A public health message could emphasize the importance of handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or elbow, and staying home when sick.
The Current Situation in China
The recent increase in HMPV cases among children in China might be attributed to several factors, including increased population density, changes in weather patterns, and reduced immunity following COVID-19 restrictions. Comparing this outbreak to previous outbreaks in other regions requires specific data on the severity, spread, and demographic impact. The Chinese authorities’ public health response likely involves increased surveillance, enhanced infection control measures in healthcare settings, and public health campaigns promoting hygiene and preventive measures.
Last Word

The rise of HMPV infections in Chinese children highlights the importance of understanding this respiratory virus and implementing preventative measures. While treatment focuses on supportive care, proactive steps like good hygiene and potentially future vaccinations are crucial. Staying informed about outbreaks and following public health guidelines is vital in protecting vulnerable populations. Let’s work together to keep kids healthy!
FAQ Section: Viral Disease HMPV Is On The Rise Among Kids In China — What Is It?
Is HMPV contagious?
Yes, HMPV spreads easily through respiratory droplets, much like the common cold.
How long does HMPV last?
The illness typically lasts one to three weeks, but recovery time varies.
Can adults get HMPV?
Yes, but it usually causes milder symptoms in adults than in children.
Are there any long-term effects of HMPV?
Most children recover fully, but severe cases can lead to pneumonia or bronchiolitis.
What’s the difference between HMPV and RSV?
Both are respiratory viruses causing similar symptoms, but they are genetically distinct.
